(Graham)
Founders: Albert Ellis (1913-2007), Aaron Beck (b.1921), Judith S. Beck (b.1954), Donald Meichenbaum (b.1940)
Goals: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) combines both CBT and behavior therapy (BT) in a short term approach using both principles and methods (Corey, 2013). CBT is the most empirical researched therapy to date. According to Beck & Weighaar 2011 (as cited by Corey, 2013), CBT and BT are different but do share some basic characteristics the most common attributes are; a collaborative relationship between client and therapist, the premise that psychological and distress is largely a function of disturbances in cognitive processes, a focus on changing cognition's to produce desired changes in affect and behavior, a present-centered, time focus, an active and directive stance by the therapist, and an educational treatment focusing on specific and structured target problems.
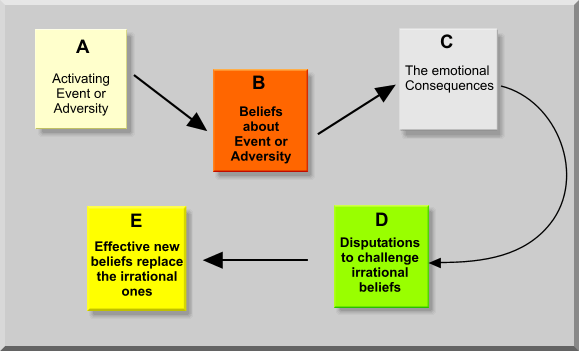
Beginning with Albert Ellis's rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT)- REBT was the first of the CBT approaches. The basic assumption of REBT is that people contribute to their own psychological problems, as well as to specific symptoms, by the rigid and extreme beliefs that hold about events and situations (Corey, 2013). The basic hypothesis is that our emotions come from our beliefs, which influence the way we react to certain life situations. Ellis's ABC model is shown below to help understand the clients feelings, thoughts, events, and behavior.
(albertellis.info/text.htm, 2008)
Cognitive methods with emotive and behavioral techniques:
- Disputing irrational beliefs
- Doing cognitive homework
- Bibliotherapy
- Changing one's language
- Psycho educational methods
- Rational emotive imagery (REI)
- using humor
- Role playing
- Shame-attacking exercises
("Aaron Beck", 2013)
Next important figure in CBT is Aaron Beck...
Beck began his work with his research on depression; CBT is an active, directive, time-limited, present-centered, problem-oriented, collaborative, structured and empirical therapy (Corey, 2013).
Basic Concepts: Concentrating on clients automatic thoughts (personal notions that are triggered by stimuli that lead to emotional responses), and cognitive distortions (faulty assumptions and misconceptions) in the "here and now" no matter the diagnosis. According to Corey 2013, the goal of this brief therapy includes providing symptom relief, assisting clients in resolving their most pressing problems, and teaching clients relapse prevention strategies.
Here is a list of some of the cognitive distortions that some people have that lead to faulty assumptions and misconceptions according to Beck and Weishaar 2011 (as cited by Corey, 2013):
- Arbitrary inferences (thinking of the worst scenario and outcome for most situations)
- Selective abstraction (consists of forming conclusions based on an isolated detail of an event)
- Overgeneralizing (holding extreme beliefs on the basis of a single incident and applying them inappropriately to dissimilar events or settings)
- Magnification and minimization (consists of perceiving a case or situation in a greater or lesser light than it truly deserves)
- Personalization (relating external events to themselves even when there is no basis for making the connection)
- Labeling and mislabeling (portraying one's identity on the basis of imperfections and mistakes made in the past and allowing them to define one's true identity)
- Dichotomous thinking (involves categorizing experiences in either or extremes)
Though REBT and CBT do have a lot in common the main difference between the two is that the client-therapist relationship is much different. Where Ellis views the therapist largely as a teacher and does not think a warm personal relationship with clients is essential, Beck liked to combine empathy and sensitivity along with technical competence (Corey, 2013).
("Donald Mechenbaum", 2002)
Another pioneer in CBT is Donald Mechenbaum's cognitive behavioral modification, which focuses on changing the client's self-verbalization's, combining elements from BT and CBT.
Mechenbaum's 1977, proposes that "behavior change occurs through a sequence of mediating processes involving the interaction of inner speech, cognitive structures and behaviors and their resultant outcomes" (as cited by Corey, 2013).
According to Mechenbaum 1977 (as cited by Corey, 2013), there is a three phase process of change:
Phase 1- Self Observation (teaching clients to become aware and observable to their own behavior)
Phase 2- Starting a new internal dialogue (changing the maladaptive cognition's that cause maladaptive behaviors)
Phase 3- Learning new skills (new coping skills will help clients modify the downward spiral of thinking, feeling, and behaving and help them regain a more positive outlook)
Another pioneer in CBT is Donald Mechenbaum's cognitive behavioral modification, which focuses on changing the client's self-verbalization's, combining elements from BT and CBT.
Mechenbaum's 1977, proposes that "behavior change occurs through a sequence of mediating processes involving the interaction of inner speech, cognitive structures and behaviors and their resultant outcomes" (as cited by Corey, 2013).
According to Mechenbaum 1977 (as cited by Corey, 2013), there is a three phase process of change:
Phase 1- Self Observation (teaching clients to become aware and observable to their own behavior)
Phase 2- Starting a new internal dialogue (changing the maladaptive cognition's that cause maladaptive behaviors)
Phase 3- Learning new skills (new coping skills will help clients modify the downward spiral of thinking, feeling, and behaving and help them regain a more positive outlook)
Stress Inoculation Training: Mechenbaum, 1997 (as cited by Corey, 2013) designed this training to help clients deal with stressful situations with his constructivist narrative perspective. This perspective focuses on the stories people tell about themselves and others regarding significant events in their lives. Mechenbaum believed in facing fears head on, first by dealing with the stress plus the thought process of whatever is causing the anxiety. The following procedures designed by Mechenbaum (as cited by Corey, 2013) below were designed to teach these coping skills;
- Expose clients to anxiety-provoking situations by means of role playing and imagery
- Require clients to evaluate their anxiety level
- Teach clients to become aware of the anxiety-provoking cognition's they experience in stressful situations
- Help clients examine these thoughts by reevaluating their self-statements
- Have clients note the level of anxiety following the reevaluation
Below I have included a youtube video with Judith Beck (Aaron Beck's daughter) explaining CBT in detail, take a look it's very insightful.
Resources
Corey, G. (2013). Theory and practice of counseling and psychotherapy. (9 ed., pp. 137-171). Belmont, CA: BROOKS/COLE CENGAGE Learning.
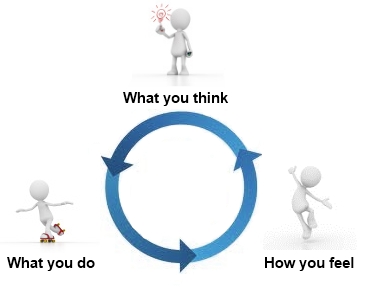
Graham, A. (n.d.). What cbt looks like. [Print Graphic]. Retrieved from http://www.annegraham.ca/cognitive-behavioral-therapy.html
(2010). Albert ellis. (2010). [Print Graphic]. Retrieved from http://mulattodiaries.wordpress.com/page/57/
(2013). Aaron beck. (2013). [Print Photo]. Retrieved from http://psychcentral.com/blog/archives/2009/09/02/a-profile-of-aaron-beck/
2002). Donald meichenbaum. (2002). [Print Photo]. Retrieved from https://www.psychotherapy.net/interview/donald-meichenbaum
Judith beck [Web]. (2008). Retrieved from http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=45U1F7cDH5k



In these situations the pharmacist can advise on how to deal with codeine withdrawal, usually through gradually reduce their codeine medication under the supervision of their GP or at a drug treatment centre.
ReplyDeleteAddiction center Indy
CBT counseling
ReplyDeleteWe offer private counseling for individaul, couples and family. Our experienced psycotherapist provide counseling for anxiety, marriage and depression etc.
Very significant Information for us, I have think the representation of this Information is actually superb one. This is my first visit to your site. Clinical Psychologist near me
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteIt's quite effective in treating major depressive disorders. Modifying thought patterns to change moods and behaviors can have a long-lasting positive impact on the patients. Cisco Distributor KSA
ReplyDeleteDG is a Leading Web Design Dubai Agency, offering scalable website development and design services for diverse verticals.
ReplyDeletePsychoeducation counseling
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing such information – please look
Psychoeducation counseling is an extremely important tool when it comes to helping people fight against mental illnesses. It is all about educating the patient and their family about what they’re going through, the treatment and process of getting better and much more and creates a safe space for the patients to talk about their difficulties much more openly.
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDelete